I have always believed that a strong sense of community is essential for a thriving society. That is why I am so captivated by the concept of tiny home village development and its ability to foster a genuine connection among its residents. By providing individuals with a small, affordable, and sustainable housing option, these communities prioritize community engagement and shared spaces, ultimately nurturing a deep sense of belonging. In this article, we will explore the concept of tiny home village development and how it is transforming the way we approach community-building.
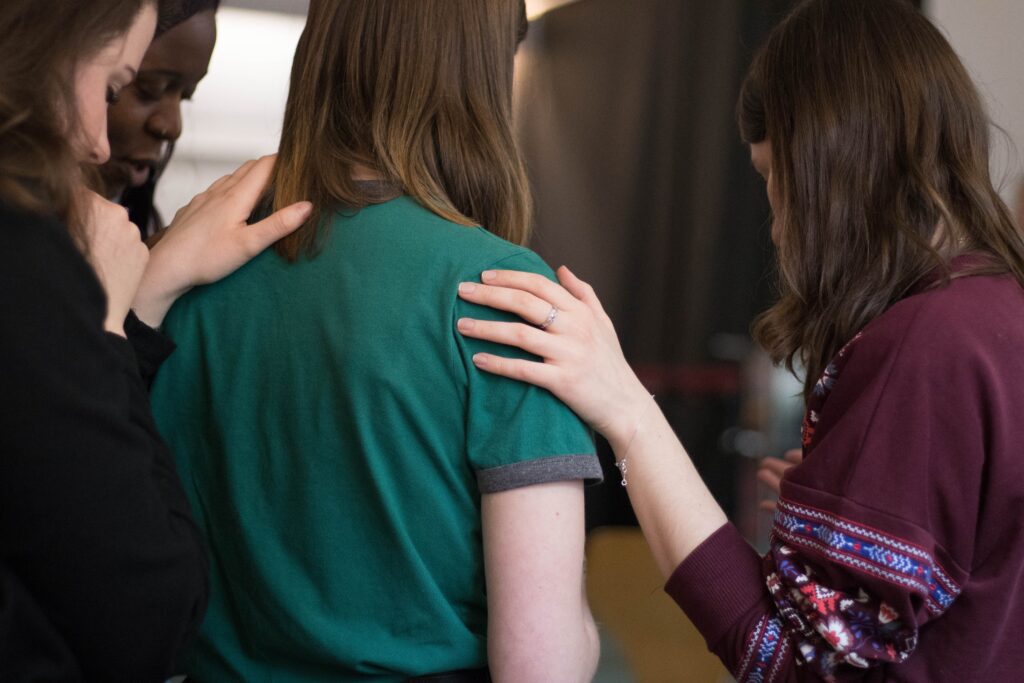
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
The Benefits of Tiny Home Village Development
As someone who has always been interested in sustainable living and community building, I am truly excited about the concept of tiny home village development. These unique communities bring together like-minded individuals who are seeking a simpler, more affordable way of life. By offering a range of benefits, including financial freedom, environmental sustainability, and a strong sense of community, tiny home villages are quickly becoming a popular option for those looking to downsize and live more intentionally.
One of the greatest advantages of tiny home village development is the financial freedom it offers. With the average cost of a traditional home skyrocketing, many people find it nearly impossible to own property or even pay exorbitant rent prices. However, tiny home villages provide an affordable alternative. The reduced size of these homes significantly lowers construction and maintenance costs, making it possible for individuals to own their own homes without the burden of a mortgage. This financial freedom allows residents to focus on other important aspects of their lives, such as pursuing their passions and enjoying meaningful experiences.
In addition, tiny home villages promote environmental sustainability. These communities emphasize minimalism, encouraging residents to live with less and reduce their ecological footprint. The small size of these homes means less energy is required for heating, cooling, and lighting, leading to lower utility bills and decreased overall energy consumption. Furthermore, many tiny home villages incorporate sustainable practices such as water conservation, composting, and the use of renewable energy sources. By embracing sustainable living, these communities actively contribute to the preservation of our planet for future generations.
Most importantly, tiny home villages offer a strong sense of community that is often lacking in modern society. In traditional neighborhoods, it is not uncommon for residents to live side by side without ever truly knowing one another. However, in a tiny home village, the tight-knit community encourages social interaction and support. The shared common spaces, such as communal gardens, gathering areas, and recreational facilities, foster a sense of belonging and encourage residents to connect with their neighbors. This sense of community creates opportunities for collaboration, shared resources, and the development of meaningful relationships. It’s a truly enriching experience that enhances the overall quality of life for those who choose to become part of a tiny home village.
This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
Designing the Layout and Architecture of a Tiny Home Village
When it comes to designing the layout and architecture of a tiny home village, careful planning and consideration are crucial. The objective is to create a community that maximizes both privacy and communal spaces, providing residents with a comfortable and harmonious living environment.
One important aspect of the layout is ensuring that each tiny home has an appropriate amount of space around it. While the goal is to promote a close-knit community, it is equally important to respect the privacy of the residents. This can be achieved by carefully positioning the homes and considering the distance between each unit. Additionally, the incorporation of outdoor areas, such as patios or decks, can provide residents with personal outdoor spaces to enjoy.
Another key consideration is the placement of communal spaces within the village. These shared spaces serve as the heart of the community, encouraging interaction and fostering a sense of belonging. Whether it’s a community garden, a common dining area, or a gathering space for events and celebrations, these spaces should be strategically located to maximize accessibility and promote social engagement.
In terms of architecture, the design of the tiny homes should not only be functional but also aesthetically pleasing. The use of sustainable materials, efficient layouts, and clever storage solutions can ensure that the homes are both comfortable and visually appealing. Additionally, incorporating elements of nature, such as natural lighting and green spaces, can contribute to creating a peaceful and serene atmosphere within the village.
Overall, designing the layout and architecture of a tiny home village requires a balance between privacy and community. By carefully considering the needs and preferences of the residents, it is possible to create a harmonious living environment that promotes social interaction while respecting individual space.
Building and Financing Tiny Home Villages
Building and financing tiny home villages can be a complex process, but with the right approach, it is achievable. Whether it’s through public-private partnerships, crowdfunding, or traditional financing options, there are several strategies that can be utilized to make these projects a reality.
One approach to building and financing tiny home villages is through public-private partnerships. Collaborating with local government agencies and nonprofit organizations can provide access to resources, expertise, and funding opportunities. This type of partnership allows for the pooling of resources and the sharing of responsibilities, making the development process more feasible and efficient. Furthermore, partnering with local entities can also help navigate through regulatory requirements and address any potential roadblocks that may arise during the project.
Crowdfunding has emerged as a popular option for financing tiny home villages. By leveraging the power of the crowd, individuals and organizations can raise funds for their projects through online platforms. This approach not only provides access to capital but also allows for the engagement of the community in the development process. Supporters can contribute to the project financially and emotionally, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the village.
Traditional financing options, such as loans and grants, are also available for tiny home village development. Approaching financial institutions, foundations, and government agencies that support affordable housing initiatives can provide access to capital to cover construction costs. It is important to present a well-developed business plan and financial projections to demonstrate the viability and sustainability of the project. Additionally, exploring partnerships with housing cooperatives or non-profit organizations that specialize in affordable housing can also open doors to funding opportunities.
In conclusion, while building and financing tiny home villages may present challenges, they are not insurmountable. By leveraging public-private partnerships, crowdfunding, and traditional financing options, these unique communities can thrive and provide affordable housing options for those seeking a simpler way of life.
Creating Community Spaces within Tiny Home Villages
Community spaces play a vital role in the success and overall experience of a tiny home village. These shared areas serve as focal points for social interaction, fostering a sense of belonging and strengthening the bonds between residents. By carefully designing and maintaining these spaces, a vibrant and inclusive community can be cultivated within the village.
One of the most common community spaces found in tiny home villages is the communal garden. These green spaces provide residents with the opportunity to connect with nature, grow their own food, and engage in communal gardening activities. Not only does this promote sustainable living practices, but it also encourages collaboration and shared responsibility. Residents can exchange gardening tips, trade produce, and build relationships while tending to their plots. The communal garden acts as a gathering place and a source of pride for the entire community.
Another important community space is a shared dining area or kitchen. These spaces allow residents to come together and enjoy meals, whether it’s a potluck dinner or a community-wide celebration. Sharing meals not only fosters a sense of community but also provides an opportunity for residents to showcase their culinary skills and cultural traditions. By creating a space where residents can comfortably cook and eat together, the village becomes a hub for sharing and connection.
Recreational facilities, such as a common clubhouse, fitness center, or outdoor play area, are also essential community spaces within a tiny home village. These areas provide opportunities for residents of all ages to engage in physical activities, promote wellness, and build relationships through shared hobbies and interests. Whether it’s yoga classes, game nights, or children’s playdates, these spaces facilitate social interaction and contribute to the overall well-being of the community.
To enhance the sense of community, the design and maintenance of these community spaces must be a collaborative effort. Involving residents in the decision-making process and encouraging their participation in the upkeep of these areas fosters a sense of ownership and pride. Additionally, organizing community events and activities within these spaces further strengthens the bonds between neighbors, creating a close-knit and supportive community.
Sustainable Living Practices in Tiny Home Villages
Sustainable living practices are at the core of the tiny home village movement. These communities aim to minimize their impact on the environment by embracing eco-friendly practices and encouraging residents to adopt sustainable habits. By incorporating innovative solutions and promoting responsible consumption, tiny home villages can serve as models for sustainable living.
One of the key elements of sustainable living in tiny home villages is energy efficiency. The small size of these homes allows for greater control over energy usage. From incorporating energy-efficient appliances and lighting to utilizing passive heating and cooling techniques, residents can significantly reduce their energy consumption. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, further enhances the sustainability of the village. These initiatives not only reduce residents’ carbon footprint but also lower utility costs, making sustainable living more accessible and affordable.
Water conservation is another crucial aspect of sustainable living in tiny home villages. Implementing practices like rainwater harvesting, low-flow fixtures, and graywater systems can significantly reduce water consumption. Residents can also be encouraged to practice mindful water usage, such as shorter showers and collecting water for plants. By prioritizing water conservation, these communities contribute to the preservation of this precious resource and help mitigate the effects of drought and water scarcity.
Waste reduction and recycling initiatives are essential components of sustainable living in tiny home villages. Residents can be educated on the importance of reducing waste, composting organic materials, and recycling to minimize landfill usage. Community-wide recycling programs and the establishment of a central composting system can facilitate responsible waste management and promote circular economy principles. By reducing waste, these communities minimize their overall environmental impact and contribute to the conservation of natural resources.
Sustainable transportation options are also encouraged within tiny home villages. By promoting alternative modes of transportation, such as walking, cycling, or carpooling, residents can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. The design of the village can incorporate pedestrian-friendly paths, bike racks, and car-sharing programs to facilitate sustainable transportation choices. Furthermore, locating the village near public transportation hubs allows residents to easily access amenities and services without the need for private vehicles.
In conclusion, sustainable living practices in tiny home villages go hand in hand with the principles of simplicity, minimalism, and environmental responsibility. By embracing energy efficiency, water conservation, waste reduction, and sustainable transportation, these communities lead by example and inspire others to adopt sustainable habits. The collective efforts of residents contribute to a greener future and a more resilient planet.
Promoting Social Interaction and Support Systems in Tiny Home Villages
A strong sense of social interaction and support is one of the defining features of tiny home villages. These communities foster a friendly and inclusive environment where residents can form deep connections, share resources, and support one another. By implementing strategies that promote social interaction and nurture support systems, tiny home villages can enhance the overall well-being and quality of life for their residents.
One of the most effective ways to promote social interaction within a tiny home village is by creating shared spaces and amenities. Common areas, such as community gardens, outdoor seating areas, and recreational facilities, serve as gathering points where residents can naturally come together and engage in meaningful conversations and activities. By strategically designing these spaces to be inviting and conducive to interaction, the village becomes a hub for socialization and connection.
Organizing regular community events and activities is another powerful tool for promoting social interaction. From potluck dinners and barbecues to movie nights and game tournaments, these events provide opportunities for residents to come together and forge relationships. By involving residents in the planning and organization of these activities, a sense of ownership and camaraderie is fostered within the community. Additionally, celebrating special occasions and holidays as a community strengthens the bonds between neighbors and creates lasting memories.
Support systems are equally important in maintaining a thriving and harmonious tiny home village. By encouraging residents to offer and receive support from one another, a sense of reciprocity and trust is established within the community. Residents can form support groups for various needs, such as wellness, gardening, or childcare. Additionally, creating a system for sharing resources, such as tools, appliances, and skills, fosters a culture of collaboration and cooperation. These support systems not only create a sense of security and belonging but also enhance the overall resilience of the community.
Communication and open dialogue are key elements in maintaining social interaction and support within a tiny home village. Establishing regular residents’ meetings or a community newsletter can facilitate information sharing, encourage participation, and address concerns in a transparent manner. Additionally, providing platforms for residents to share their ideas, suggestions, and feedback regarding the village’s development and activities promotes a sense of ownership and empowerment. By fostering an environment of open communication, residents feel heard, valued, and actively engaged in the community’s well-being.
In conclusion, promoting social interaction and support systems is vital in creating a thriving and inclusive tiny home village. By designing shared spaces, organizing community events, and nurturing support networks, these communities become vibrant and fulfilling places to live. The bonds formed within the village foster a deep sense of connection, support, and belonging that enhances residents’ overall well-being and quality of life.
Addressing Challenges and Concerns in Tiny Home Village Development
While the concept of tiny home village development has gained popularity and recognition for its numerous benefits, it is important to acknowledge and address the challenges and concerns that may arise during the planning and implementation stages. By proactively navigating these obstacles, the potential for success and longevity of a tiny home village can be maximized.
One of the primary challenges in tiny home village development is finding suitable locations for these communities. Zoning and land-use regulations vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and many areas have not yet adapted their regulations to accommodate tiny home villages. This can present significant challenges in finding land that is appropriately zoned and compliant with local regulations. Developers and advocates may need to work closely with government officials and community stakeholders to explore potential amendments to existing regulations or to identify suitable sites for development.
Securing financing for tiny home village projects can also be a challenge. Traditional financing sources may be hesitant to invest in these unique communities due to their unconventional nature and lack of a proven track record. Moreover, the perceived risks associated with tiny homes, such as potential issues with quality and durability, can further deter lenders. Overcoming these challenges may require creative financing solutions, such as public-private partnerships, crowdfunding, or alternative lending options, that are better aligned with the specific needs and circumstances of tiny home village development.
The social acceptance and stigma surrounding tiny homes can present another obstacle. Many people still hold negative stereotypes and misconceptions about tiny homes, associating them with poverty or substandard living conditions. This stigma can lead to resistance from local communities and NIMBY (not in my backyard) opposition. Educating the public about the benefits and positive aspects of tiny home villages, including their potential to address affordable housing issues and promote sustainable living, is crucial in overcoming this challenge. Engaging in community outreach and public relations efforts can help dispel misconceptions and build support for these innovative housing solutions.
Infrastructure considerations are yet another challenge in tiny home village development. Ensuring access to basic utilities, such as water, electricity, and sewage, may require additional planning and investment, especially in remote or undeveloped areas. Collaborating with utility providers and conducting thorough feasibility studies can help identify potential infrastructure challenges and develop solutions. Incorporating sustainable practices, such as off-grid energy systems or water conservation measures, can further address these concerns and enhance the village’s long-term viability.
Lastly, maintaining a sense of community and managing potential conflicts within the village can be an ongoing challenge. As the village grows and evolves, it is important to establish clear guidelines and protocols for residents’ behavior and community governance. Implementing a transparent and inclusive decision-making process, such as community councils or committees, can help address conflicts and ensure the village’s continued harmony. Regular communication, conflict resolution, and ongoing community-building efforts are essential in maintaining a positive and supportive environment within the village.
In conclusion, while there are challenges and concerns associated with tiny home village development, they can be effectively addressed through careful planning, collaboration, and community engagement. By proactively navigating regulatory obstacles, securing suitable financing, addressing stigma, and considering infrastructure needs, tiny home villages can overcome these challenges and create thriving and sustainable communities.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations for Tiny Home Villages
Legal and regulatory considerations are paramount in the successful development and operation of tiny home villages. Adhering to local laws and regulations not only ensures compliance but also fosters a positive relationship with the broader community and government entities. Understanding and addressing these considerations from the outset is essential in creating a legally sound and sustainable tiny home village.
One of the primary legal considerations is the zoning and land-use regulations that govern the location and development of tiny home villages. Zoning laws vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, and it is important to research and understand the specific regulations in the area of interest. Some areas may have specific provisions for tiny homes, while others may require variances or amendments to existing zoning regulations. Working closely with local government officials and community stakeholders can help navigate these legal complexities and ensure compliance with the relevant zoning requirements.
Building codes and safety regulations are another crucial aspect of legal compliance in tiny home village development. The construction of tiny homes must meet the applicable building codes, including regulations pertaining to structural integrity, fire safety, and basic amenities. Given the unique nature of these homes, it may be necessary to collaborate with local building officials to ensure that they are familiar with and able to accommodate the specific requirements of tiny homes. Engaging the services of experienced architects, engineers, and contractors who specialize in tiny home construction can help ensure compliance with building codes and regulations.
Another legal consideration is the establishment of legal entities and governance structures for the tiny home village. The creation of a legal entity, such as a homeowners association (HOA) or a housing cooperative, can provide a formal framework for managing the village and addressing legal responsibilities. The legal entity will often be responsible for establishing and enforcing community guidelines, collecting fees, and managing shared resources and amenities. Engaging legal counsel experienced in community organization and homeowner association law can help navigate these legal complexities and develop the necessary legal documents and agreements.
Furthermore, it is important to consider local permitting and licensing requirements for the operation of a tiny home village. Ensuring compliance with health permits, business licenses, and any other applicable permits is crucial in avoiding legal issues and potential fines. It is advisable to consult with local government agencies and obtain the necessary permits and licenses before the village becomes operational. Regular inspections and ongoing compliance with local regulations contribute to the overall safety, legitimacy, and long-term viability of the tiny home village.
Additionally, legal considerations should also include ensuring that residents have legally enforceable rights and protections. Secure and affordable tenancy agreements or long-term lease agreements are essential in providing a stable living environment for residents. Consulting with legal professionals experienced in landlord-tenant law and affordable housing regulations can help develop fair and legally sound agreements that protect the rights of both the residents and the village.
In conclusion, legal and regulatory considerations are fundamental to the success and sustainability of tiny home village development. Adhering to zoning and land-use regulations, building codes, and safety requirements ensures compliance and fosters positive relationships with local government entities. Establishing legal entities and governance structures, obtaining necessary permits and licenses, and protecting residents’ rights further contribute to the legal soundness and long-term viability of the tiny home village.
Evaluating the Success and Impact of Tiny Home Villages
Evaluating the success and impact of tiny home villages is crucial in understanding the effectiveness of these unique communities and identifying areas for improvement. By collecting and analyzing data, feedback, and experiences, valuable insights can be gained to inform future development and enhance the overall success of tiny home villages.
One key aspect of evaluating the success of a tiny home village is measuring resident satisfaction and well-being. Conducting regular surveys or interviews with residents can provide valuable feedback on their quality of life, sense of community, and overall satisfaction with the village. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and guide future decision-making processes. Additionally, monitoring key social indicators, such as social connectedness, mental health, and overall life satisfaction, can provide quantitative data to assess the impact of the village on residents’ well-being.
Tracking the economic impact of the tiny home village is also important. Evaluating the financial stability and economic outcomes of the residents, such as changes in income, debt reduction, and financial security, can provide insights into the affordability and long-term viability of the village. Additionally, studying the local economic effects, such as job creation, increased tourism, and support for local businesses, can help assess the overall economic benefits and contributions of the tiny home village to the surrounding area.
Another important aspect to evaluate is the impact of the tiny home village on the environment. Collecting data on energy consumption, water usage, waste management, and other sustainability indicators can provide insights into the ecological footprint of the village and its contribution to environmental preservation. By comparing these indicators to traditional housing options, a clear picture emerges of the environmental benefits and sustainability of tiny home villages.
Furthermore, assessing the social impact of the tiny home village is crucial. Connecting with local community stakeholders, such as neighboring residents, businesses, and local government officials, can provide insights into the village’s acceptance, integration, and relationships with the surrounding community. Feedback from these stakeholders can help identify areas for strengthening community engagement and promoting positive interactions.
Analyzing the long-term viability and sustainability of the tiny home village is also essential. Monitoring the ongoing financial stability, governance structures, and maintenance of the village ensures that it remains a thriving and desirable place to live. Assessing the longevity and adaptability of the village to changing economic, environmental, and social conditions can inform future development efforts and enhance the overall sustainability of the village.
In conclusion, evaluating the success and impact of tiny home villages is a multi-faceted process that involves assessing resident satisfaction, economic outcomes, environmental contributions, social impact, and long-term viability. Collecting and analyzing data from residents, local stakeholders, and key social, economic, and environmental indicators helps inform decision-making processes and guides future development efforts. By continuously evaluating and learning from the experiences of existing tiny home villages, the potential for success and positive impact can be maximized.
Inspiring Community Engagement and Advocacy for Tiny Home Villages
Inspiring community engagement and advocacy is crucial in promoting the development and success of tiny home villages. By raising awareness, building partnerships, and mobilizing community support, it becomes possible to overcome challenges, navigate regulatory obstacles, and foster a supportive environment for these unique communities.
One of the most effective ways to inspire community engagement and advocacy is through education and raising awareness. Hosting information sessions, workshops, or community forums that provide accurate and reliable information about tiny home villages can help dispel misconceptions and foster a deeper understanding of the benefits they offer. Engaging local media outlets, social media platforms, and local influencers can further amplify the message and reach a broader audience. Education enables individuals to make informed decisions and actively support the development of tiny home villages.
Building partnerships with local government entities, nonprofit organizations, and community leaders is another powerful strategy for inspiring community engagement and advocacy. Collaborating with these stakeholders helps gain credibility, access to resources, and support for the development of tiny home villages. By actively engaging in open communication and building positive relationships, it becomes possible to address concerns, navigate regulatory processes, and identify potential funding opportunities.
Engaging residents and the broader community in the development process is essential in inspiring ownership and advocacy for tiny home villages. Soliciting community input through surveys, town hall meetings, or community design workshops allows individuals to voice their ideas, concerns, and aspirations for the village. This participation fosters a sense of ownership and investment in the community, inspiring a collective effort to ensure its success. Welcoming public input and incorporating it into the development plans also builds trust and facilitates community buy-in.
Engaging with existing tiny home villages and their residents can serve as a source of inspiration and support for future developments. Organizing community tours or hosting open house events in established villages provides an opportunity for individuals to see firsthand the benefits of these communities. Additionally, establishing a network for tiny home village advocates and residents to connect and share experiences can create a sense of camaraderie and provide a platform for knowledge exchange.
Advocacy at both the local and broader policy level is essential in creating an enabling environment for tiny home villages. Educating elected officials and policymakers about the benefits of tiny home villages and their potential to address affordable housing issues and promote sustainable living can influence the development of supportive policies and legislation. Engaging in grassroots advocacy, such as organizing letter-writing campaigns, attending public hearings, and voicing support at community meetings, can help shape public opinion and drive positive change.
In conclusion, inspiring community engagement and advocacy is crucial in promoting the development and success of tiny home villages. By raising awareness, building partnerships, and mobilizing community support, it becomes possible to overcome challenges, navigate regulatory obstacles, and foster a supportive environment for these unique communities. Engaging and empowering individuals to become advocates for tiny home villages not only benefits the immediate community but also promotes affordable housing and sustainable living on a broader scale.



This image is property of images.unsplash.com.
